HVAC duct making machines play a central role in modern ventilation and air distribution systems. Rather than referring to a single piece of equipment, the term usually describes a complete set of machines used to fabricate sheet metal ducts efficiently, accurately, and at scale. Understanding how these machines work together is essential for HVAC manufacturers planning capacity upgrades or automation.
This article provides a clear and practical overview of HVAC duct making machines, covering core equipment types, production workflows, automation levels, and selection considerations—without unnecessary technical overload.

What Is an HVAC Duct Making Machine?
An HVAC duct making machine refers to the equipment used to convert flat sheet metal into finished air ducts for heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning systems. These machines handle key processes such as forming, cutting, edge preparation, and assembly.
In real-world factories, duct production is rarely completed by a single machine. Instead, manufacturers rely on a combination of duct fabrication equipment, arranged either as standalone workstations or as an integrated production line. The level of automation depends on production volume, duct type, and labor availability.
Main Equipment Used in HVAC Duct Manufacturing
Although configurations vary, most HVAC duct making systems include several core categories of machines, each responsible for a specific production stage.
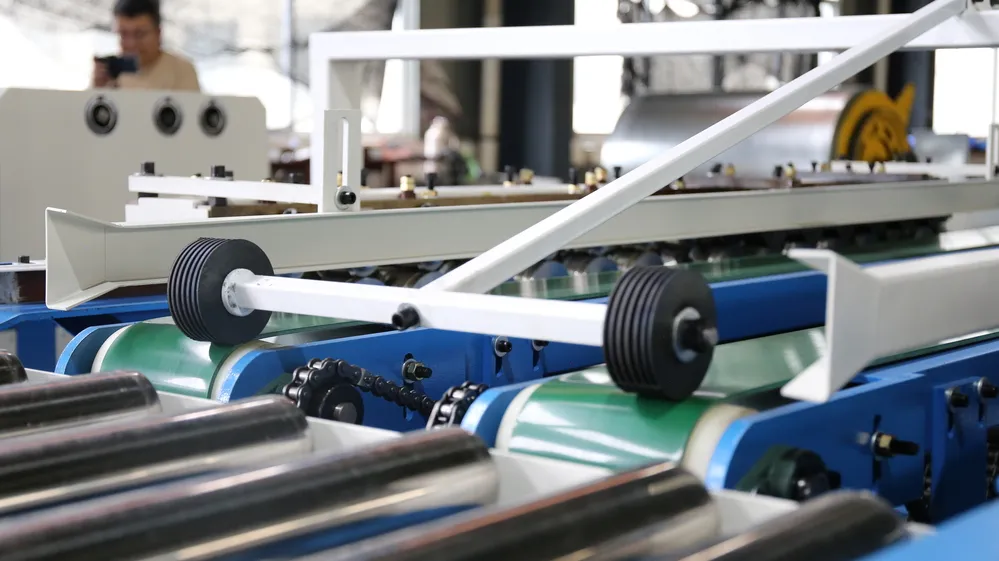
Sheet Metal Forming and Shaping Equipment
Forming equipment is responsible for shaping flat sheets into duct sections. This category typically includes duct forming machines, bending units, and rolling machines. These machines create the basic geometry of rectangular or round ducts while maintaining dimensional accuracy.
Consistent forming is critical because any deviation at this stage directly affects downstream processes such as seam closing and installation alignment.
Edge Processing and Seam Preparation Machines
Edge preparation ensures that duct sections can be securely joined. Machines used in this stage focus on strengthening edges and preparing connection profiles.
Processes such as grooving, seam preparation, and flange forming are designed to improve structural integrity while maintaining smooth airflow inside the duct. Automated edge processing also reduces reliance on skilled manual labor and improves repeatability across batches.

Cutting, Punching, and Notching Machines
Cutting and punching machines prepare ducts for assembly and installation. These machines handle length cutting, corner notching, and hole punching for accessories such as dampers or mounting brackets.
Accuracy at this stage reduces fitting issues on-site and helps manufacturers maintain consistent production standards, especially when working with prefabricated HVAC systems.
Automatic vs Semi-Automatic Duct Making Systems
HVAC duct making machines can be arranged in semi-automatic setups or fully automatic duct production lines, depending on factory requirements.
Semi-automatic systems usually consist of independent machines operated by workers who transfer materials manually between stations. This approach offers flexibility and lower initial investment but may limit output consistency and scalability.
Automatic systems integrate multiple processes into a continuous workflow. Automatic duct production lines reduce handling time, stabilize output quality, and are better suited for high-volume manufacturing environments where efficiency and labor optimization are priorities.
How These Machines Work Together in Production
In a typical production workflow, sheet metal is first fed into forming equipment to create duct profiles. The formed sections then pass through edge preparation stages, where seams and connection features are added. Afterward, cutting and punching machines finalize dimensions and prepare the ducts for assembly or shipment.
The key advantage of a well-planned HVAC duct making system lies in process coordination. When machines are properly matched in speed and capability, bottlenecks are minimized, and material flow remains stable throughout the line.

Key Factors When Choosing HVAC Duct Making Equipment
Selecting the right HVAC duct making machine setup involves more than comparing machine specifications. Manufacturers should consider several practical factors:
Production volume requirements and future scalability
Duct types, such as rectangular, round, or spiral
Automation level and available workforce
Factory layout and space constraints
After-sales support and technical service
A balanced equipment selection ensures long-term efficiency rather than short-term cost savings.
Typical Applications in HVAC Manufacturing
HVAC duct making machines are widely used across different manufacturing scenarios. Common applications include commercial building ventilation, industrial exhaust systems, prefabricated duct workshops, and OEM HVAC production facilities.
Each application places different demands on output capacity, flexibility, and automation, making equipment configuration a strategic decision rather than a one-size-fits-all choice.
Conclusion: Building an Efficient Duct Production Setup
An HVAC duct making machine should be understood as a production system rather than a single device. By combining forming, edge processing, and cutting equipment into a coherent workflow, manufacturers can achieve stable quality, predictable output, and improved operational efficiency.
Whether adopting a semi-automatic setup or investing in a fully integrated production line, the key lies in selecting equipment that aligns with production goals, factory conditions, and long-term growth plans.
FAQ
An HVAC duct making machine is used to convert flat sheet metal into finished ducts for ventilation systems. It handles forming, edge preparation, cutting, and assembly tasks in a coordinated production workflow.
Typical machines include duct forming machines, duct bending and rolling units, edge processing equipment such as duct grooving and RAS seam closing, cutting and punching machines, and optional automated feeding systems.
Automatic duct production lines integrate multiple processes into a continuous workflow, reducing manual handling, minimizing bottlenecks, and maintaining consistent output quality. Standalone machines require more operator intervention and may produce variable results.