Flange forming plays a critical role in rectangular duct manufacturing, especially in modern HVAC systems where strength, sealing performance, and installation efficiency are equally important. Unlike seam-based connections, flange connections create a standardized edge around the duct, allowing sections to be bolted together securely during installation. As HVAC projects move toward higher efficiency and faster on-site assembly, flange forming has become a core process in duct production lines.
This article explains what flange forming is, how the process works in real manufacturing environments, the most common flange types, and how flange forming fits into automated duct production.

What Is Flange Forming in Rectangular Duct Manufacturing?
Flange forming is a metal forming process used to create a rigid edge, or flange, along the perimeter of a rectangular HVAC duct. This flange serves as the connection interface between duct sections, frames, or accessories. Instead of relying solely on folded seams or mechanical locking, flange forming creates a defined profile that improves alignment and load distribution.
In rectangular duct production, flange forming is typically performed after the duct panel edges are cut and shaped. The formed flange becomes an integral part of the duct structure, enabling consistent connections across large-scale HVAC installations.
Why Flange Forming Is Used for Rectangular HVAC Ducts
Rectangular ducts are widely used in commercial and industrial HVAC systems due to space constraints and airflow design requirements. Flange forming supports these applications by offering several practical advantages:
- Improved structural rigidity: The formed flange reinforces duct edges, reducing deformation during handling and installation.
- Reliable sealing performance: Flange connections work effectively with gaskets and sealants to minimize air leakage.
- Standardized installation: Consistent flange dimensions allow installers to assemble duct sections quickly using bolts or clamps.
For large projects, these benefits translate directly into reduced labor time and improved system reliability.
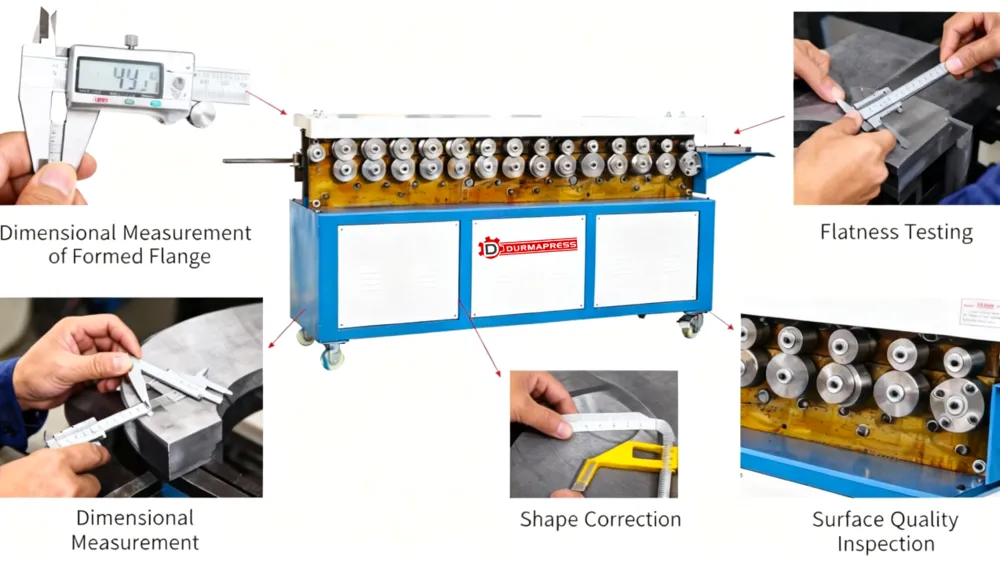
How the Flange Forming Process Works
Although flange profiles may vary, the flange forming process generally follows a consistent sequence in rectangular duct manufacturing.
Edge Preparation Before Flange Forming
Before flange forming begins, duct panels are cut to size and their edges are prepared. This may include straightening, deburring, or preliminary folding, depending on the flange design. Proper edge preparation ensures accurate flange geometry and reduces tool wear during forming.
Flange Rolling and Shaping
The prepared duct edges pass through forming rollers or dies that gradually shape the metal into the required flange profile. This roll forming approach allows controlled deformation without cracking or thinning the sheet metal. In many production lines, the forming operation is continuous, supporting stable quality at high throughput.
Flange Size and Profile Control
Flange width, angle, and thickness must remain consistent to ensure proper alignment during installation. Modern flange forming equipment uses mechanical guides or CNC-controlled adjustments to maintain dimensional accuracy across different duct sizes.
Common Flange Types Used in Rectangular Ducts
Different HVAC standards and project requirements lead to the use of various flange designs.
TDF and TDC Flanges
TDF (Transverse Duct Flange) and TDC (Transverse Duct Connector) systems are among the most widely used integrated flange solutions. These flanges are formed directly from the duct sheet metal, eliminating the need for separate angle iron frames.
Angle Iron Flanges
Angle iron flanges are traditional external frames attached to duct edges. While they require additional components and assembly steps, they remain common in heavy-duty or large-dimension ducts where extra strength is required.
Other Integrated Flange Profiles
Some manufacturers use proprietary or customized flange profiles designed to match specific installation systems or regional standards. These profiles are often optimized for compatibility with automated production lines.
Equipment Used for Flange Forming
Flange forming can be performed using different types of equipment, depending on production scale and automation level.
Standalone Flange Forming Machines
Standalone machines are typically used in small to mid-sized workshops. Operators feed duct sections manually, and the machine forms the flange along the edges. This setup offers flexibility but requires more labor input.In many workshops, flange forming machines are used alongside duct grooving machines to handle different duct connection requirements efficiently.
Integrated Flange Forming Units in Automatic Duct Lines
In high-volume manufacturing, flange forming units are integrated into automatic duct lines. In these systems, flange forming is synchronized with cutting, grooving, and bending operations, allowing continuous production with minimal manual handling.
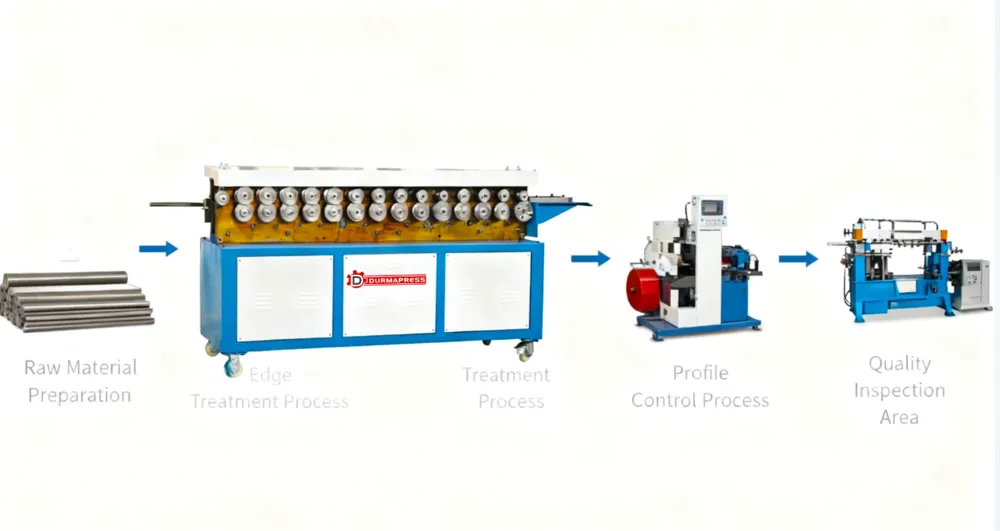

Applications of Flange Forming in HVAC Duct Manufacturing
Flange forming is used across a wide range of HVAC applications, including:
- Commercial buildings such as offices, malls, and hospitals
- Industrial facilities with large airflow requirements
- Standardized HVAC projects requiring modular duct assembly
Its adaptability makes flange forming suitable for both custom duct fabrication and mass production environments.
Flange Forming vs Other Duct Connection Method
Flange Forming vs Duct Grooving
Duct grooving creates a mechanical joint along duct edges, while flange forming focuses on creating an external connection interface. Flange connections are often preferred when ducts must be disassembled or adjusted during installation.Unlike flange forming, duct grooving creates a mechanical joint along the duct edge, which is commonly used in automated HVAC duct production for fast assembly.
Flange Forming vs Seam-Based Connections
Seam-based connections rely on folded or locked edges for strength. For seam-based connections, RAS seam closing is often applied to lock and reinforce folded duct seams, especially in rectangular duct manufacturing. While effective for certain duct sizes, seam connections may offer less flexibility compared to flange systems when handling large rectangular ducts.
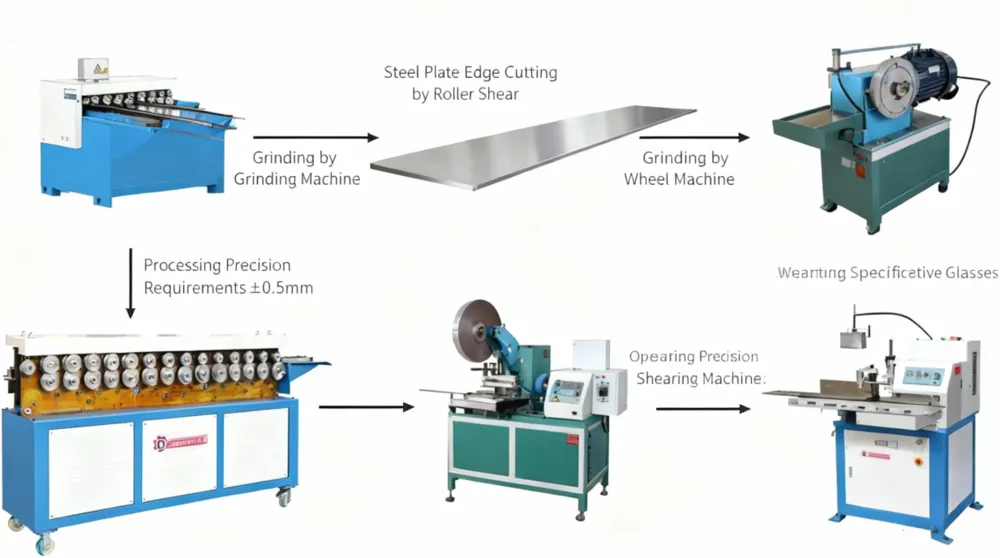
Flange Forming in Automated Duct Production Lines
As HVAC manufacturing moves toward automation, flange forming is increasingly integrated into complete duct production lines. In high-volume manufacturing, flange forming is commonly integrated into automatic duct lines, where cutting, grooving, bending, and flange forming are completed in a continuous process. Automated systems improve consistency, reduce labor dependency, and support higher output volumes. In these environments, flange forming operates as part of a coordinated process that includes cutting, grooving, bending, and seam closing.
Conclusion: The Role of Flange Forming in Modern Duct Manufacturing
Flange forming is a fundamental process in rectangular duct manufacturing, providing strong, standardized connections that support efficient installation and long-term performance. Whether performed as a standalone operation or integrated into an automated duct line, flange forming remains essential to modern HVAC production workflows.
FAQs About Flange Forming in Rectangular Ducts
Integrated flange systems such as TDF and TDC are widely used due to their efficiency and compatibility with automated production.
Yes. In modern automatic duct lines, flange forming can be fully automated and synchronized with other manufacturing steps.
Galvanized steel is the most common material, but stainless steel and aluminum can also be used depending on project requirements.


