In HVAC duct production, seam integrity directly affects duct strength, air tightness, and long-term performance. Among various seam forming and locking methods, RAS seam closing is a widely used technique for reinforcing rectangular duct seams, especially in traditional and semi-automated manufacturing environments.
This article explains what RAS seam closing is, how the process works, the types of machines involved, and where it fits in modern HVAC duct production. The focus is on technical understanding rather than product promotion, helping manufacturers and engineers evaluate when RAS seam closing is the right solution.
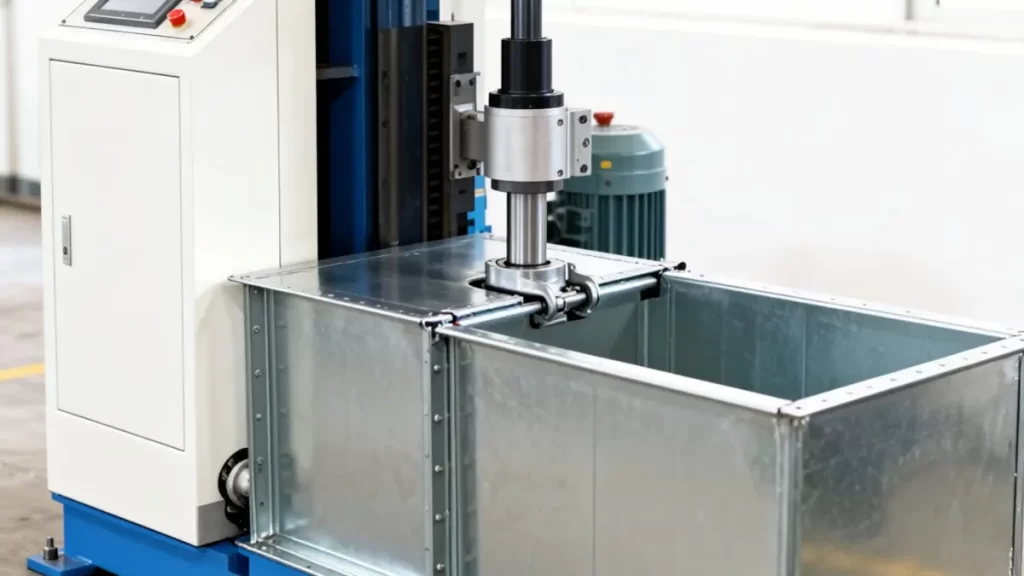

What Is RAS Seam Closing?
RAS seam closing is a mechanical process used to lock and reinforce pre-formed seams in rectangular HVAC ducts. The term “RAS” commonly refers to seam profiles and closing methods derived from European duct fabrication standards, where seams are folded and mechanically pressed to create a secure joint.
In duct manufacturing, seam closing is a critical step that transforms a formed duct section into a rigid, sealed structure. RAS seam closing ensures that the seam remains stable under airflow pressure and during installation.
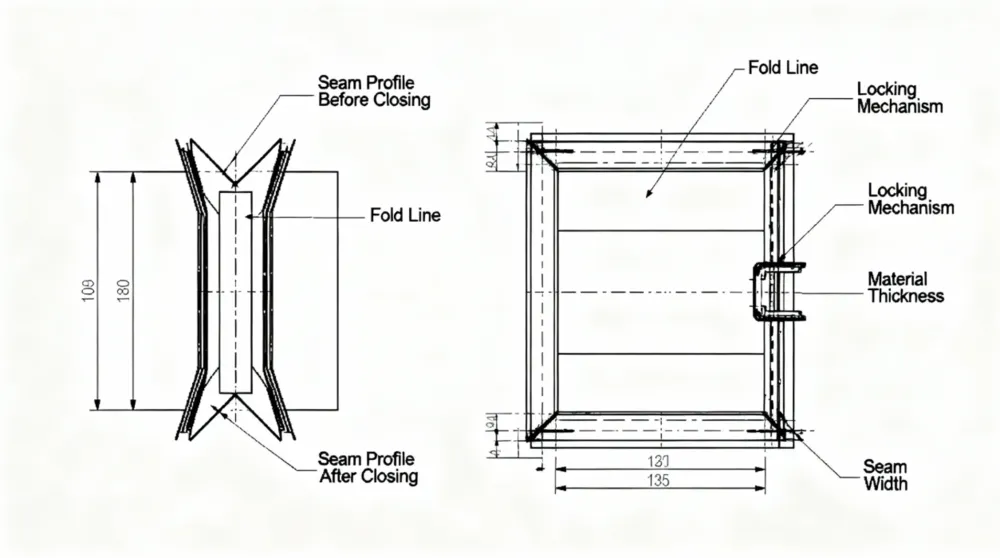
How RAS Seam Closing Works in Duct Manufacturing
The RAS seam closing process follows a controlled sequence designed to maintain consistency and seam strength.Before seam closing, duct edges are typically prepared through the duct grooving process, which ensures proper alignment and consistent seam formation.
Seam Preparation Before Closing
Before closing, duct panels are formed with predefined seam profiles. Proper preparation ensures that the seam edges align correctly, allowing the closing operation to produce a uniform and reliable joint.
Mechanical Closing and Locking
During seam closing, mechanical rollers or pressing tools apply force along the seam length. This action folds and locks the seam profile, creating a tight mechanical connection without welding or additional fasteners.
Seam Reinforcement and Consistency
Once closed, the seam gains increased rigidity and resistance to deformation. Consistent seam closing is essential for maintaining dimensional accuracy across multiple duct sections, especially in batch production.
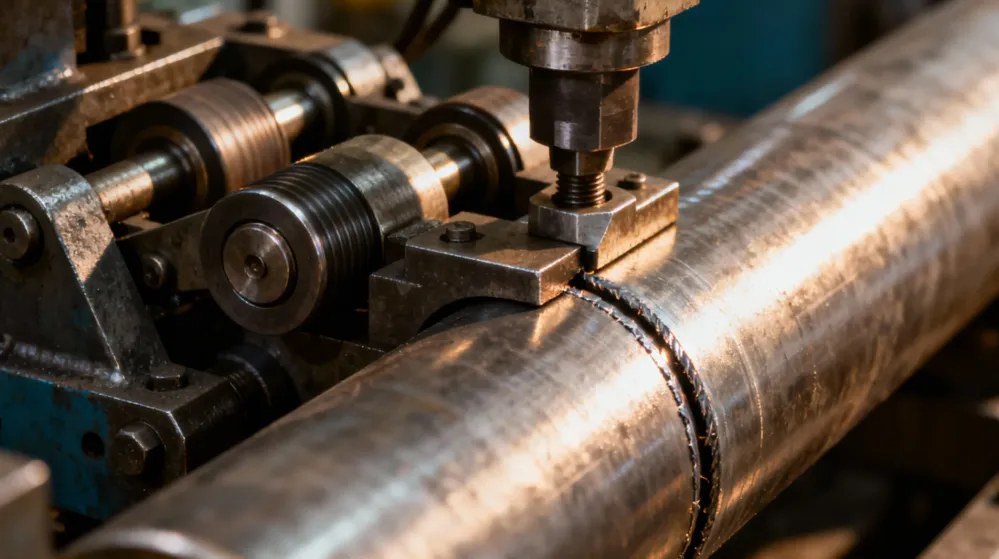

RAS Seam Closing Machines and Equipment
Different levels of automation are available depending on production volume and workflow requirements.In many production setups, edge preparation is handled by a dedicated duct grooving machine before the seam closing operation begins.
Manual and Semi-Automatic RAS Seam Closers
Manual and semi-automatic machines are commonly used in small to medium-sized HVAC workshops. These machines offer flexibility and are suitable for custom duct fabrication or low to medium production volumes.
RAS Seam Closing Units in Duct Production Lines
In more structured production environments, RAS seam closing units can be integrated into duct forming lines. While not fully automated in the same way as modern seam-closing systems, they help improve efficiency and reduce operator variability.
Applications of RAS Seam Closing in HVAC Duct Production
RAS seam closing is typically used in the following scenarios:
- Rectangular HVAC duct fabrication
- Low- and medium-pressure duct systems
- Custom or project-based duct manufacturing
Its reliability and relatively simple operation make it a practical choice where full automation is not required.

RAS Seam Closing vs Other Duct Seam Methods
Understanding how RAS seam closing compares with other seam techniques helps manufacturers choose the appropriate method.Compared with seam-based connections, systems using a flange forming machine rely on edge flanges rather than locked seams to join duct sections.
RAS Seam Closing vs Pittsburgh Lock Seam
Pittsburgh lock seams are widely used for fast manual assembly, while RAS seam closing focuses on controlled mechanical reinforcement. RAS seams often provide more uniform seam quality in standardized production environments.
RAS Seam Closing vs Automated Seam Closing Systems
Automated seam closing systems are designed for high-volume, fully automatic duct lines. In contrast, RAS seam closing offers greater flexibility and lower equipment complexity, making it suitable for workshops that prioritize adaptability over maximum throughput.
RAS Seam Closing in Automatic Duct Lines
In modern automatic duct lines, RAS seam closing is less common than fully automated seam systems. However, it may still be used in hybrid production setups or as a supplementary process for specific duct sizes or configurations.In high-capacity factories, seam closing is often integrated into an automatic duct line, where forming, grooving, and seam operations are synchronized.
Its role in these environments depends on production scale, required seam standards, and overall line integration strategy.
Is RAS Seam Closing Still Relevant in Modern HVAC Manufacturing?
Despite increasing automation, RAS seam closing remains relevant in many HVAC manufacturing scenarios. Its durability, ease of maintenance, and adaptability make it a practical solution for manufacturers who require consistent seam quality without investing in fully automated systems.
Rather than being obsolete, RAS seam closing continues to serve as a reliable option within a broader range of duct fabrication technologies.
Conclusion: Understanding the Role of RAS Seam Closing
RAS seam closing plays an important role in HVAC duct production by providing a reliable method for reinforcing duct seams. While automation continues to advance, this process remains valuable for manufacturers seeking a balance between consistency, flexibility, and investment cost.
Understanding how RAS seam closing works and where it fits in the production workflow helps manufacturers make informed decisions about duct fabrication methods and equipment selection.
FAQs About RAS Seam Closing
RAS seam closing is primarily used for rectangular HVAC ducts, particularly in low- and medium-pressure systems.
It is generally more suitable for low- to medium-pressure applications. High-pressure systems often require additional reinforcement or alternative seam methods.
RAS seam closing can be partially automated, but it is typically not as integrated as seam closing systems designed specifically for fully automatic duct lines.


